What is cache?
- Patterns for deciding what to store, when to store it, and when to invalidate it.
- Stores copies of data in a location that can be accessed more quickly than the original source.
- Readily availability of frequently accessed information makes systems respond to user requests faster.
- Improves overall performance and user experience.
- Also contributes to scalability, and availability.
Caching Strategies
Cache-aside (Lazy Loading)
Use cases: 大部分 CRUD 场景 high read, low write
- Component read cache
- Component read DB upon cache miss
- Component update cache
- 写的时候先更新 DB 再删除缓存(注意不是更新,否则并发很容易错)

Pros:
- 实现简单、侵入性小,和现有数据库模型耦合低,失败时最多回退到查 DB,不会把系统搞炸
- Cache only stores what’s needed
Cons:
- First/misses request is slow
- 并发情况下读写之间存在短暂不一致窗口,不是强一致
- 在高并发下容易出现缓存击穿(同一个 key 失效瞬间,大量请求打到 DB)
- 需要自己处理好删除缓存的时机
Read-Through
Use cases: Stable data and high read
- Component read cache
- Cache read DB upon miss

Pros:
- Component logic is simple; easy to scale reads
- 缓存和存储的一致性由缓存层保证,对业务代码友好
Cons:
- Cache needs additional processing(通常意味着中间件或自研层)
- 缓存和 DB 强耦合,缓存一旦出问题,影响很大
Write-Through
Use cases: Strong read consistency (e.g., shopping cart)
- Component write cache
- Cache write DB

Pros
- Cache is always fresh
- No stale reads
- Reads have low latency
Cons:
- Writes have high latency 缓存没有加速写
- Cache becomes a write bottleneck(因为和数据库强耦合)
- Infrequent data is also stored in the cache
Write-Back (Behind)
Use cases: High throughput systems
- Component keep write cache constantly
- Cache write DB at intervals 异步写回

Pros:
- 写性能极高,可以合并写、削峰填谷,对 DB 极其友好
Cons:
- Cache and DB are eventually consistent
- Data lost if cache goes down
- Infrequent data is also stored in the cache
- 实现复杂,需要 WAL、重试、顺序保证等机制
Time-to-live (Expiration)
Use cases: Cashing data that changes periodically (e.g., session data)
Basically the same with cache-aside, except that expired cache entries are removed
Pros:
- Automatic clean-up of stale data; reduces the risk of serving outdated data.
Cons:
- Expiration storms if many keys expire at the same time
- Cached data may expire before it’s no longer needed, resulting in cache misses.
Refresh Ahead
Use cases: Obvious hot key and stable visiting pattern (首页配置、榜单、热点内容)
设置 TTL,但在即将过期前,后台线程或异步任务提前刷新 cache(或者每次访问时都刷新),而不是等用户请求触发 miss
Pros:
- 显著降低缓存击穿概率
- 用户请求几乎永远命中 cache
- Latency is stable
Cons:
- May refresh some no-longer-accessed keys
- 一致性是最终一致
- 实现复杂,需要后台任务、调度
Local Cache + Distributed Cache
Use cases: High QPS, latency-sensitive (e.g., recommendation, ads)
进程内缓存(如 Caffeine / Guava) → Redis → DB
Pros:
- Read latency is low
- 大幅降低 Redis 压力
Cons:
- Consistency hazard
- 异步失效通知、版本号 / 短 TTL
- 本地缓存失效、容量、垃圾回收都要处理
Cache Problems
Cache Avalanche 缓存雪崩
大量 key 在同一时间失效。
原因:
- 同一批 key 设置了相同 TTL
- Redis down
- cache service 抖动 / unavailable
Solution:
- Random TTL 打散失效时间
- 多级缓存
- 熔断、限流、降级
- 通过主从节点构建 Redis 高可靠 cluster
Hotspot Invalid 缓存击穿
Cache 中某个 hot key 过期时,大量请求访问该数据,全部 cache miss 后访问 DB,DB 容易被高并发请求冲垮。
Solution:
- 互斥锁 singleflight,cache miss 时只有一个业务线程去查 DB ,然后更新缓存;其他线程等待锁释放后再读 cache
- 前面提到的 fresh ahead:不给 hot key 设置过期时间,后台异步更新 cache,或者在快要过期时提前通知后台线程更新 cache 以及重新设置 TTL
- 一致性是最终一致
Cache Penetration 缓存穿透
高频请求的数据在 cache 和 DB 里都不存在。(请求 userId = -1,请求不存在的订单号,恶意扫描 ID 空间)
Solution:
- 限制非法请求,在 API 入口校验请求参数
- 缓存空值,在 DB 查到不存在的值时也缓存
value = null- 如果攻击者不断换 key(比如扫 ID),缓存会被塞满大量空值,所以一般要配合容量限制、TTL 很短
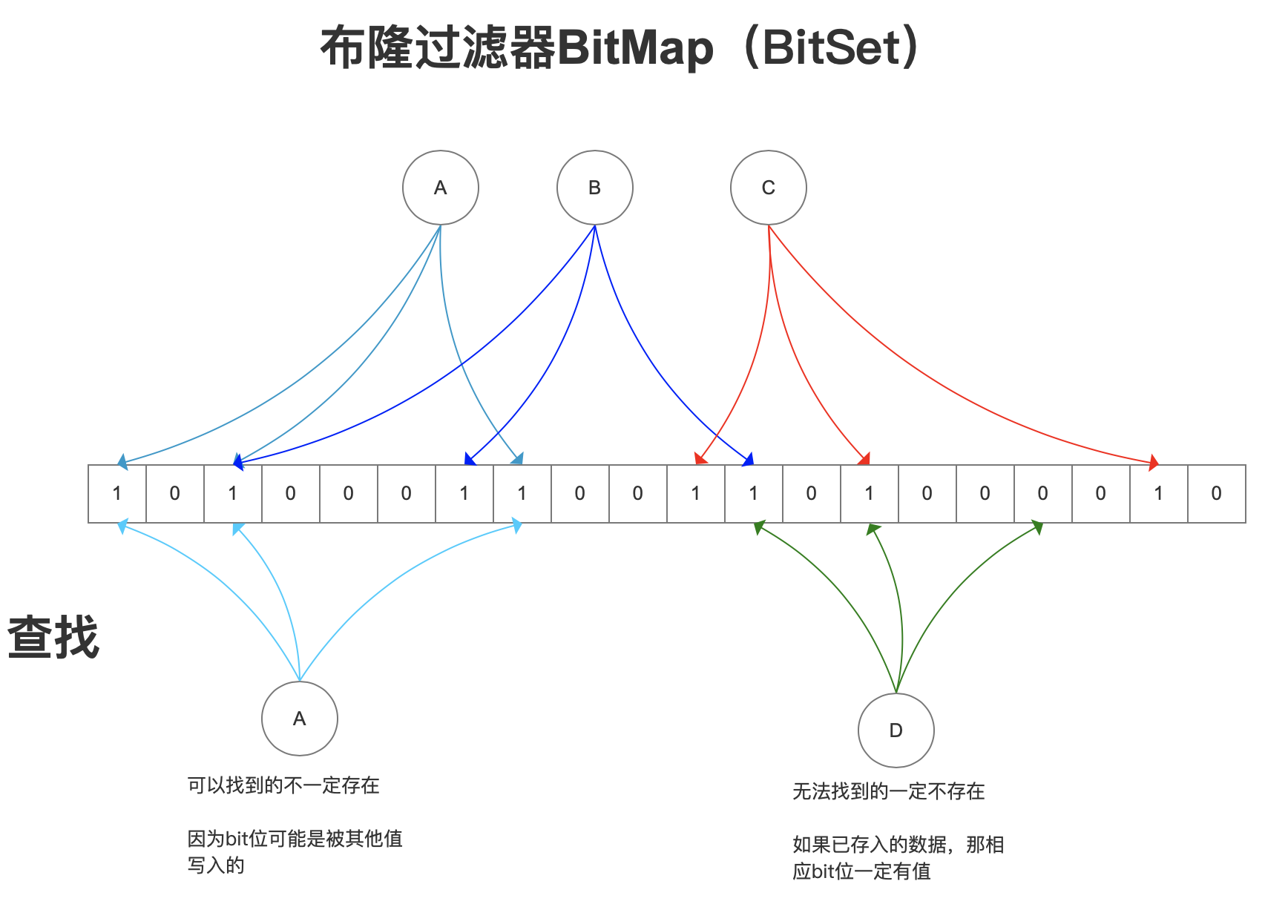
- Bloom Filter:快速判断这个 key 是否有可能存在
- Potential false positives,but NO false negatives
- 有维护成本,不适合频繁变更的数据,实现复杂度比缓存空值高;一般在 ID 空间大、攻击风险高时使用
Bloom Filter
It uses a bit array and multiple hash functions to enable fast lookups (constant time) with minimal memory. Cache 的前置防护,减少 DB 压力
A Bloom filter with \(m\) bits and \(k\) hash functions is initialized to all zeros. To add an item \(x\), \(k\) hash functions \(h_{1}(x),\dots,h_{k}(x)\) map it to \(k\) array positions, which are then set to 1.
Amazon Use Case
Cache Aside
- Product detail pages
- Search autocomplete
- Personalization recommendations
Read Through
- AWS API Gateway caching 缓存下游服务的响应
- Internal service frameworks that wrap data access with caching
Write Through
- Shopping cart service
- Inventory availability service 保证缓存里的库存和数据库保持同步,减少库存超卖风险
Write Back
- User activity counters 点赞、播放数、浏览量
- Metrics aggregation / Analytics events
- Recommendation feature updates
TTL
- Session tokens
- Search results 可能变化较快
- API Gateway
- Rate limiting counters
- Featured flag / A-B test config