Program Analysis
Static Analysis excels at finding certain defects:
- Security: Buffer overruns, improperly validated input …
- Memory safety: Null dereference, uninitialized data …
- Resource leaks: Memory, OS resources …
| Static Analysis | Dynamic Analysis |
|---|---|
| Requires only source code | Requires successful build + test inputs |
| Conservatively reasons about all possible inputs and program paths | Observes individual executions |
| Reported warnings may contain false positives | Reported problems are real, as observed by a witness input |
| Can, in principle, report all warnings of a particular class of problems | Can only report problems that are seen. Highly dependent on test inputs. Subject to false negatives |
| Advanced techniques can prove certain complex properties, but rarely run in CI due to cost | Advanced techniques like symbolic execution can prove certain complex properties, but rarely run in CI due to cost |
Soundness and Completeness in Static Analysis
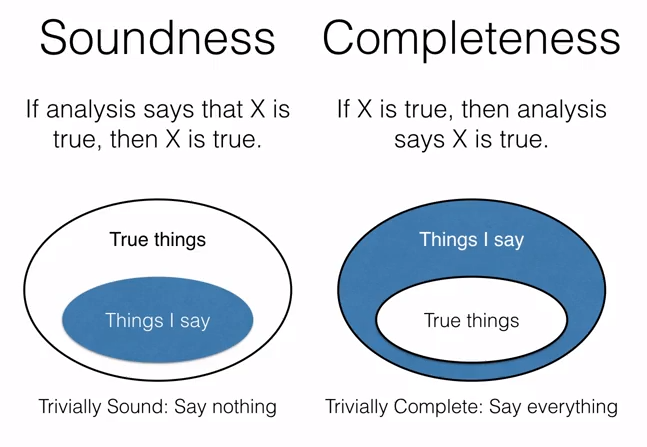
What static analysis can and cannot do:
- Type-checking is well established
- Checking for problematic patterns in syntax is easy and fast
- Reasoning about termination is impossible in general (halting problem)
- Reasoning about exact values is hard, but conservative analysis via abstraction is possible
- Verifying advanced properties is possible but expensive
Static Analysis
Formatting Linters
Use shallow static analysis to enforce formatting rules
Pattern-Based Linters
Pattern-Based Analysis evaluates program syntax against a set of rules.
Matches syntactic patterns (via abstract syntax tree) to identify likely mistakes and API misuses
- Good at finding use of disallowed and deprecated APIs, dangerous language features, and obvious mistakes
- Can only find issues for which there is a corresponding rule / pattern
Challenges:
- The analysis must produce few or (better yet) zero false positives
- The analysis needs to be really fast
- You can’t just “turn on” a particular check
Type-Based Analysis
Memory-safe doesn’t imply type safety.
- Add Types to Existing Code via Annotations
- Enrich Type Systems via Annotations
- layer additional semantics on top of the base type system
- e.g.
@Nullable, @NonNull
- Refinement Types
- restrict not only based on structure but also on values
@Refinement("positive > 0")
Value Analysis
Taint Analysis
Track values through a program and prevents untrusted data from reaching sensitive locations.
void processRequest() {
@Tainted String input = getUserInput();
input = validate(input); executeQuery(input);
}
public void executeQuery(@Untainted String input) {
}
@Untainted public String validate(String userInput) {
}
Abstract Interpretation / Value Analysis
Computes a sound over-approximations of program behavior in terms of an abstract domain.
Static Analysis for Everything Else
Static analysis isn’t just for source code; If it’s machine readable, we can statically analyze it!
- Dependencies & Supply Chain
- Typosquatting
- Config, CI, and Infrastructure-as-Code